ガウス記号は[x]で表され、実数xを超えない最大の整数を表します。
ガウス記号を含む問題は関数の連続・不連続を問う問題で頻出するがその際、極限値の捉え方が少し難しくなります。
理解を深めるために、ガウス記号の定義と共に、関数f(x)において、ガウス記号を含む、または含まない関数の極限を下で解いてみるので、参考にしてみてください。
ガウス記号の定義ガウス記号[math][x]=n[/math]において、次の定義が成立する
・[math]n[/math]は実数xの整数部分である
・[math]n[/math]は実数xを超えない最大の整数である
・整数[math]n[/math]は実数xに対して[math]n \leq x \leq n + 1[/math]を満たす
・[math]n[/math]は実数xの整数部分である
・[math]n[/math]は実数xを超えない最大の整数である
・整数[math]n[/math]は実数xに対して[math]n \leq x \leq n + 1[/math]を満たす
例題
[math]f(x)=x[/math]
[math]\lim_{x \rightarrow \pm 0}f(x)[/math]
[math]= \lim_{x \rightarrow \pm 0} x[/math]
[math]= \lim_{x \rightarrow \pm 0} x[/math]
[math]=0[/math]
[math]\lim_{x \rightarrow + 0}[f(x)][/math]
[math]= \lim_{x \rightarrow + 0}[x][/math]
[math]= \lim_{x \rightarrow + 0}[x][/math]
+から限りなく0へ近づくの意(…5,4,3,2,1,0.5,0.2,…[math]\xcancel{0}[/math])
※[0.2]を0に近い値とするならば、実数0.2を超えない整数部分は0なので
[0.2]=0となる。
[0.2]=0となる。
[math]=0[/math]
[math]\lim_{x \rightarrow – 0}[f(x)][/math]
[math]= \lim_{x \rightarrow – 0}[x][/math]
[math]= \lim_{x \rightarrow – 0}[x][/math]
-から限りなく0へ近づくの意(…-5,-4,-3,-2,-1,-0.5,-0.2,…[math]\xcancel{0}[/math])
※[-0.2]を0に近い値とするならば、実数-0.2を超えない整数部分は-1なので
[-0.2]=-1となる。
[-0.2]=-1となる。
[math]=-1[/math]
[math]y= [x][/math]の図
※赤ラインが[math]y= [x][/math] (赤の白抜き丸はその点を取らない),青の点線が[math]y=x[/math]
上の[math]y= [x][/math]の図を見てもらえばわかると思いますが、
+から近づいた場合は0が最大の整数、-から近づいた場合は-1が最大の整数になる。
[math]f(x)=x+ \dfrac{1}{3} [/math]
[math]\lim_{x \rightarrow \pm 0} f(x)[/math]
[math]=\lim_{x \rightarrow \pm 0} \big(x + \dfrac{1}{3} \big) [/math]
[math]=\lim_{x \rightarrow \pm 0} \big(x + \dfrac{1}{3} \big) [/math]
[math]= \dfrac{1}{3} [/math]
[math]\lim_{x \rightarrow \pm 0} [f(x)][/math]
[math]=\lim_{x \rightarrow \pm 0} [ \big(x + \frac{1}{3} \big)] [/math]
[math]=\lim_{x \rightarrow \pm 0} [ \big(x + \frac{1}{3} \big)] [/math]
…[math]-\dfrac{8}{3}, -\dfrac{5}{3}, -\dfrac{2}{3},0[/math],…, [math] \xcancel{\dfrac{1}{3}}[/math]
[math]= 0[/math]
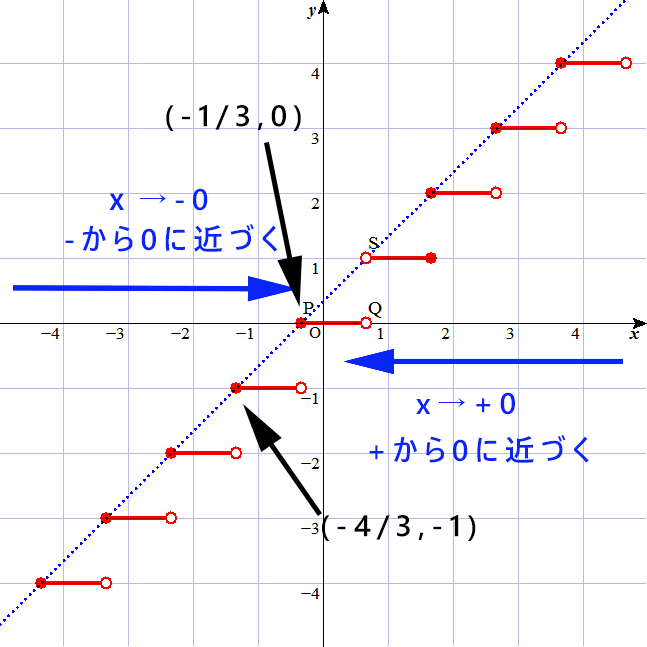
[math]y=[x+ \dfrac{1}{3} ][/math]の図
※赤ラインが[math]y=[x+ \dfrac{1}{3}][/math] (赤の白抜き丸はその点を取らない),青の点線が[math]y=x+ \dfrac{1}{3}[/math]
上の[math]y=[x+ \dfrac{1}{3}] [/math]の図を見てもらえばわかると思いますが、
+から近づいた場合はy=0が最大の整数、-から近づいた場合もy=0が最大の整数になる。
[math]f(x)=3x[/math]
[math]\lim_{x \rightarrow \pm 0} f(x)[/math]
[math]=\lim_{x \rightarrow \pm 0} 3x[/math]
[math]=\lim_{x \rightarrow \pm 0} 3x[/math]
[math]=0[/math]
[math]\lim_{x \rightarrow + 0}[f(x)][/math]
[math]=\lim_{x \rightarrow + 0} [3x][/math]
[math]=\lim_{x \rightarrow + 0} [3x][/math]
…,12,9,6,3,0.1,…[math]\xcancel{0}[/math]
[math]=0[/math]
[math] \lim_{x \rightarrow – 0}[f(x)][/math]
[math]=\lim_{x \rightarrow – 0} [3x][/math]
[math]=\lim_{x \rightarrow – 0} [3x][/math]
…,-12,-9,-6,-3,-0.1,…[math]\xcancel{0}[/math]
[math]=-1[/math]
[math]y=[3x][/math]の図
※赤ラインが[math]y=[3x][/math] (赤の白抜き丸はその点を取らない),青の点線が[math]y=3x[/math]
上の[math]y=[3x][/math]の図を見てもらえばわかると思いますが、
+から近づいた場合はy=0が最大の整数、-から近づいた場合はy=-1が最大の整数になる。






コメント